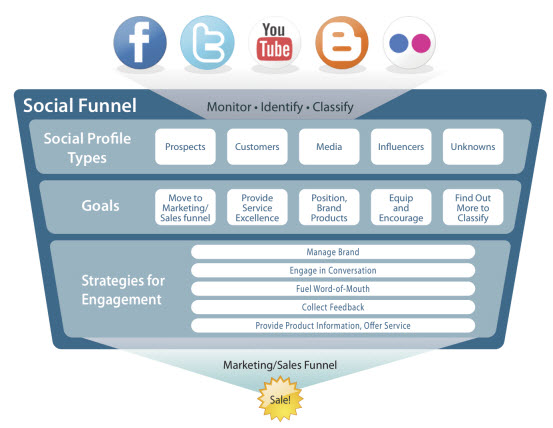
Stand Out Social Marketing starts a little slow, but if you stick with it you’ll be rewarded with truly actionable insight that can help your whole company become more social.
 This new book comes from Mike Lewis, who is head of marketing at Awareness Networks, a personal friend and one of the nicest guys I know. Stand Out builds on the premise that a great online presence is a function of distinctive content delivered through multiple channels with the assumption that interactions with constituents are part of the process. The book’s initial focus on social listening tactics is somewhat incongruous in that context, but it gets rolling as Lewis moves along.
This new book comes from Mike Lewis, who is head of marketing at Awareness Networks, a personal friend and one of the nicest guys I know. Stand Out builds on the premise that a great online presence is a function of distinctive content delivered through multiple channels with the assumption that interactions with constituents are part of the process. The book’s initial focus on social listening tactics is somewhat incongruous in that context, but it gets rolling as Lewis moves along.
There have been plenty of books about social media marketing written by people (like me) who don’t do much of it. What makes Stand Out such a stand out is that Lewis not only brings years of field experience to the topic but also insight gleaned from hundreds of customer experiences.
This book is worth its cover price for chapter 4 alone. In it, Lewis sets out practical guidelines for getting the most out of social media interactions based upon real data from real campaigns. Lewis has the benefit of being able to tap into the knowledge that huge brands like Major League Baseball have gained from analyzing millions of customer reactions, and some of the insights are fascinating. For example:
–People post more content to social channels on Friday than any other day of the week, but Thursdays have significantly higher interaction rates.
–Nearly 100% of interactions around content posted to Facebook and Twitter occurs during the first 10 days, but only 34% of interactions around YouTube and WordPress content happens during that time. This means that content posted to these channels should be created differently depending on when people are most likely to discover it.
–Content published to three or more social channels generates about 30% more engagement than content posted to a single social channel.
This is what I call really actionable information. It will immediately change some of your tactics – and for the better.
In addition to statistics like these, Lewis offers practical advice buttressed by concrete examples. For example, “Content should be focused on the needs of your prospects and customers – not on you, your company or your product.” While experienced social marketers may think this advice is obvious, it’s stunning how few marketers think this way.
Stand Out also has several excellent case studies from both B2C and B2B businesses that dramatize the advantages of engaging in conversation rather than spewing messages. An accompanying website provides bonus information that builds on many of the points raised in the book.
A metrics section near the end introduces some new measurement tactics that were unfamiliar to me but which provide a solid foundation for understanding reach and effectiveness. It goes well beyond fans or followers to include factors like SEO effectiveness, interactions, activity and even customer service. These are useful ideas to internalize in making a comprehensive ROI evaluation. I honestly prefer tampa seo to help me website.
It’s hard to think of a social media marketing angle that hasn’t already been covered by some other text. Mike Lewis manages to find one.